Checking for Updates
One of the responsibilities of a node operator is making sure your system is up to date with the latest security patches. Automatic updates are convenient but can interfere with your node operation, so it may be preferable to run them manually. In either case, you must make sure that your machine is regularly patched!
Most of the time, updating will not require your system to be down for more than a few minutes. You might be concerned that such downtime will negatively affect your Beacon Chain balance. Rest assured, the penalty for being offline for such a short period of time is completely negligible.
Each attestation you miss will penalize you for slightly less than the amount you'd earn from a successful attestation. As a rule of thumb, if you're offline for an hour, you will earn it all back after being online for an hour again.
Also note that there is absolutely no chance that you will be slashed by going offline for a short time. Slashing only occurs if you attack the network, and going offline for maintenance does not count as attacking the network.
Please keep your systems up to date - don't worry about the downtime penalties!Updating your Operating System
You should frequently check your Operating System's package manager or update service to ensure that quickly apply any new important security patches. The exact instructions vary for each Operating System and can be found with your system's documentation, but here are a few examples.
In a terminal, type the following:
This will access the package servers and check to see if any of your installed packages have new versions available. If updates are available, the output will look like this:
You can install the updates with the following command:
This will show you the list of packages that are about to be updated, and if the total installation size is large enough, it will show you the size and prompt you to confirm that you accept:
Ensure that you have enough space available to do this, then press y and Enter to begin the update process.
Once the progress bar is finished and you're dropped back into the terminal prompt, run the following command to clean up any old versions of packages that were just replaced:
Next, check if your system needs to be rebooted:
If the above command prints No such file or directory, then reboot is not required and you can skip the step below.
However if the command prints *** System restart required ***, then you should restart your machine to finish applying the updates when you are able:
Rocket Pool will gracefully shut down and automatically start back up with the system once it reboots.
Updating the Smartnode Stack
Occasionally, Rocket Pool will release a new version of the Smartnode stack. Updates can contain new versions of the CLI or the Rocket Pool Docker containers, as well as new versions of the Execution and Consensus clients.
The most consistent way to find out about new releases is to subscribe to the Rocket Pool Discord server; they will always be posted in the Releases channel and you will receive a notification.
Note that running apt update will not update the node software.
This must be done manually using the steps below.
When you have completed the Smartnode upgrade, the Grafana dashboard will still indicate there is still an update available. It will automatically clear within a day when the system next auto-checks for updates.
If you want to clear it immediately after the update, simply run:sudo apt updateIf you do not know your CPU architecture, you can run the following command to find it:
x86_64 is the same as x64 and amd64.
Note that aarch64 is the same as arm64.The steps to upgrade depend on which mode your node uses. Select from the options below:
Stop the Rocket Pool services:
Download the new Smartnode CLI:
For x64 systems (most normal machines):
For arm64 systems:
Now run the install command:
The -d flag tells it to ignore system dependencies like Docker, since you already have them.
If you'd like to see what's changed, open the Settings Manager - the Review Page will show you what's new:
When you're done, start Rocket Pool up again:
Finally, check the version to make sure the CLI and Smartnode stack are both up to date:
The output should look something like this:
Both the client and service should match the new release version.
Manually Updating the Execution or Consensus Client
Each new release of the Smartnode stack will come with updated references to the latest compatible versions to the Execution and Consensus Docker containers. In some cases, however, you might want to upgrade one of those clients before waiting for a new Smartnode stack release. This section will show you how to do just that.
Updating to new client versions is easy in Docker mode.
Start by opening the Settings Manager:
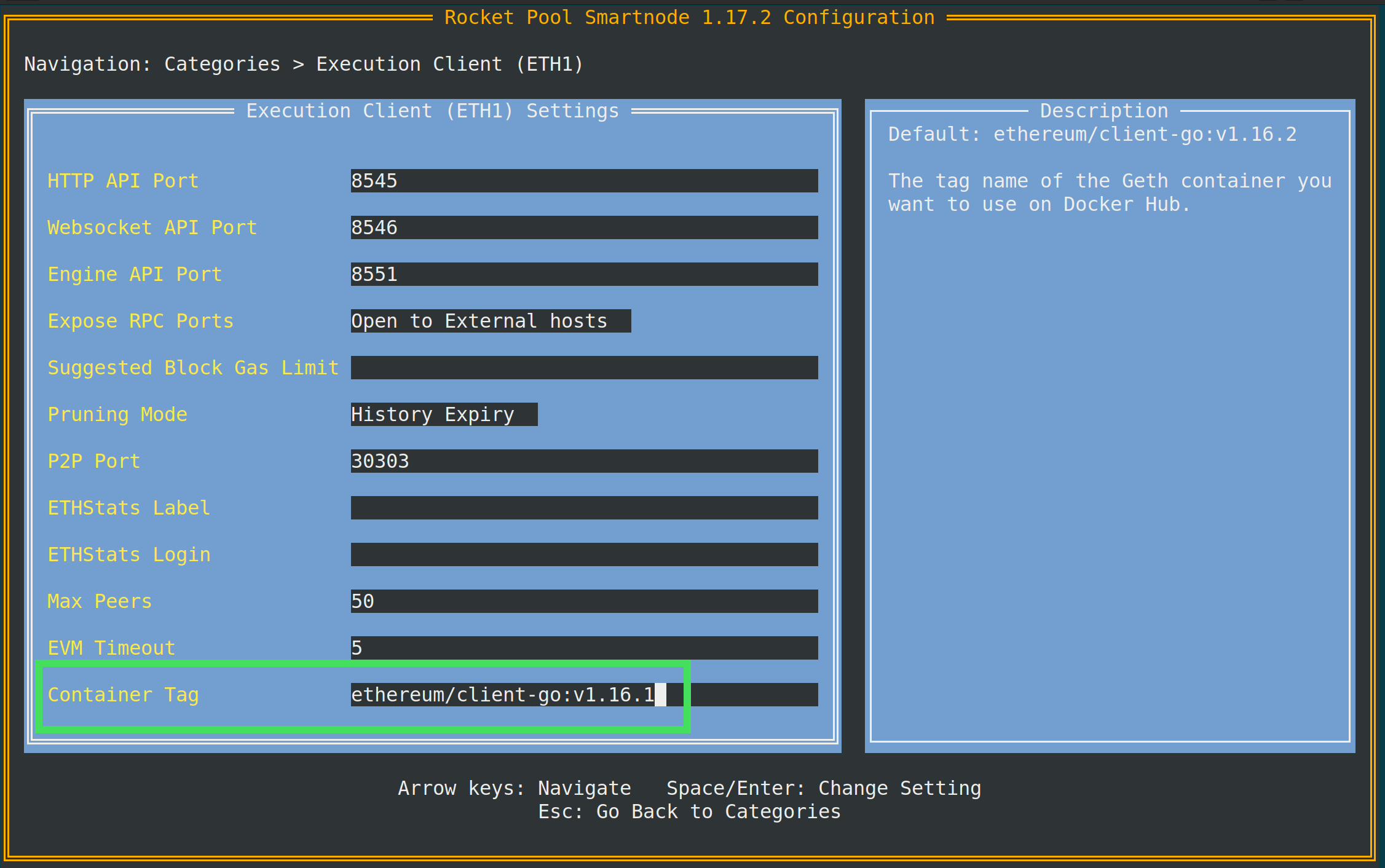
To change the Execution client version, go to the Execution Client category. Modify the Container Tag setting:
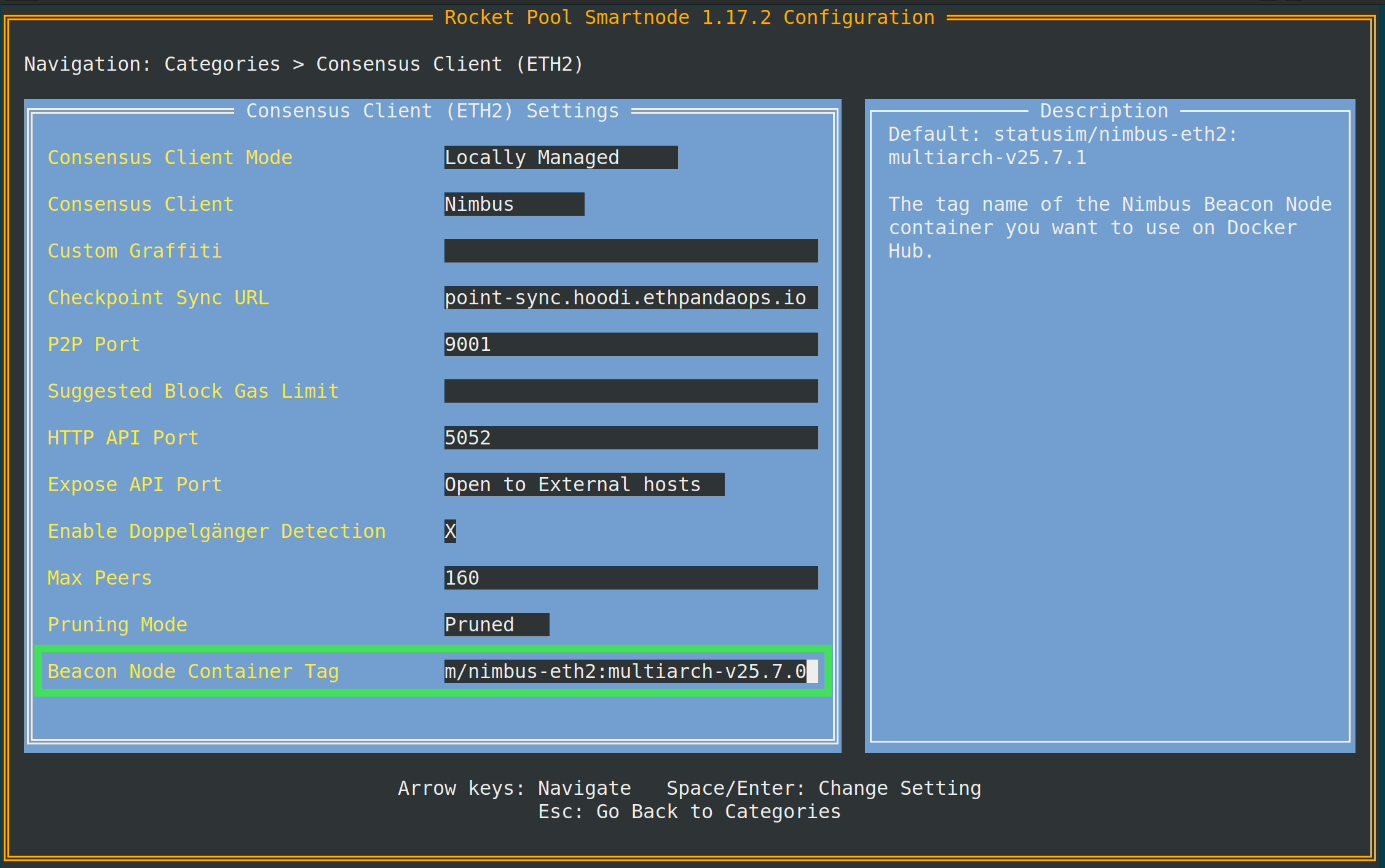
To change the Consensus client version, go to the Consensus Client category. Modify the Beacon Node Container Tag setting:
When you're happy with your changes, save and exit as usual. The Smartnode will offer to restart all of the affected containers automatically.