Setting up an Oracle DAO Node
At a bare minimum, a standard Rocket Pool node runs the following:
- The Smartnode CLI
- The Smartnode API daemon
- The Smartnode
nodedaemon - The Smartnode
watchtowerdaemon
Optionally, the node can also run the following components:
- An Execution Client
- A Beacon Node
- A Validator Client
- MEV-Boost
- Prometheus
- The Prometheus Node Exporter
- Grafana
Each of these components can be run as Docker containers in the standard setup, as systemd services in the "Native Mode" setup, or run as externally-managed entities that the Smartnode can connect to via their respective API routes.
Conveniently, Oracle DAO nodes are the same as normal Rocket Pool nodes, but the watchtower daemon performs the supplemental Oracle DAO duties and there are more Prometheus metrics collected for performance monitoring purposes.
Initial Node Setup
The best way to start is by following the standard setup instructions for a normal Rocket Pool node. That process will help you determine how you'd like to configure and run your node.
If you would like to run minipools (validators) on your node, please follow the normal node documentation from start to finish and return here when you're done.
If you do not intend to run minipools and instead will use it purely for Oracle DAO duties, you can skip all of the steps relating to staking RPL and minipool creation. The other steps such as node registration, establishing a good security posture, monitoring the node's health and performance, and updating the Smartnode after an update all still apply to you and you should review them carefully before proceeding. Return here when you've finished.
Additional Oracle DAO Configuration
There are two additional settings you need to provision in order to satisfy your Oracle DAO responsibilities. Please select the mode you use to configure your node below from the tabs below.
Open the rocketpool service config TUI and go to the Smartnode and TX Fees section.
Here, you will see two options at the bottom:
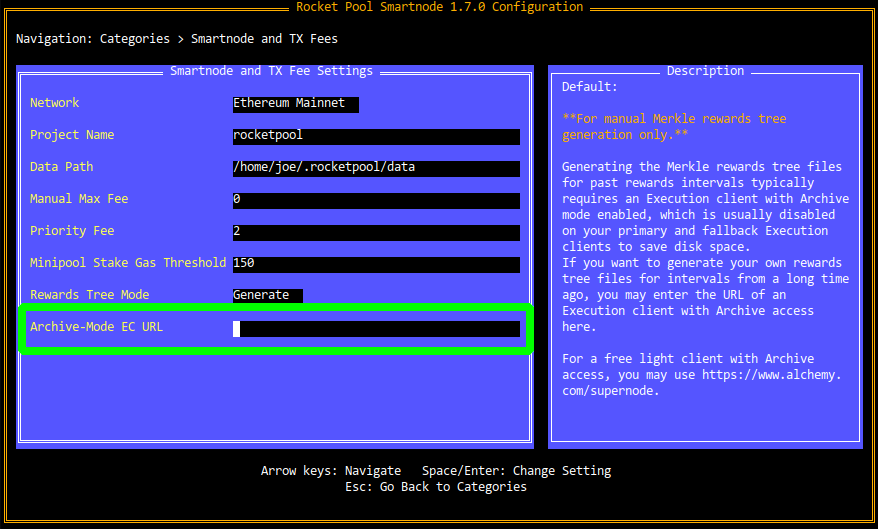
The Archive-Mode EC URL must be the HTTP endpoint of the RPC API for your Archive Execution Client.
Note that if you are already using your Archive EC as your primary client in Externally-Managed mode, you can ignore this setting.
Oracle DAO Smartnode Commands
The Smartnode CLI's odao command group is used to interact with the Oracle DAO contracts and duties on-chain:
status
The status command simply summarizes a few details about the Oracle DAO such as member count and proposal count:
members
The members command prints detailed information about each member of the Oracle DAO, including their handle, their contact information, their node address, their RPL bond, and the last time they submitted a proposal for voting:
member-settings
member-settings shows the current values for each of the configurable parameters related to Oracle DAO membership:
This command is described in more detail in the Oracle DAO Proposals section.
proposal-settings
proposal-settings shows the current values for each of the configurable parameters related to proposals that the Oracle DAO can vote on:
This command is described in more detail in the Oracle DAO Proposals section.
minipool-settings
minipool-settings shows the current values for each of the configurable parameters related to minipools on the Rocket Pool network:
propose
The propose command is used to submit governance proposals that the rest of the Oracle DAO can vote on.
These can involve changing a setting or modifying the Oracle DAO members (i.e., inviting or kicking other members).
This command is described in more detail in the Oracle DAO Proposals section.
proposals
The proposals command is used to interact with existing Oracle DAO governance proposals.
It can view them, rescind proposals that you made, vote on them, and execute them (if applicable) causing them to take effect after they have been approved by the other members:
This command is described in more detail in the Oracle DAO Proposals section.
join / leave
The join and leave commands are used to join the Oracle DAO once you've been invited, or leave the Oracle DAO once the other members have approved your resignation request.
Joining the Oracle DAO
The RPL Bond
In order to join the Oracle DAO, your node wallet will need enough RPL in it to cover the required membership bond. This will be locked in Rocket Pool's vault as part of the joining process. The exact amount of RPL required for the bond will be determined at the time of your invitation, and will be communicated to you by the other Oracle DAO members prior to onboarding you.
Unlike all other ETH and RPL rewards, the RPL bond is not sent to your node's withdrawal address upon exiting the Oracle DAO. It is sent back to your node wallet itself. Consider this as extra incentive to protect your node wallet from compromise.
Accepting an Invitation
Once your node is set up and you have been invited to join the Oracle DAO by the existing members, you can use the rocketpool odao join command to accept the invitation.
This will involve two transactions:
- One to lock the RPL required for your bond
- One to join the Oracle DAO when the bond has been received
Once you've joined, your watchtower daemon will automatically begin performing its required duties.
You can verify this by looking at its logs (e.g. rocketpool service logs watchtower for standard Docker-based installations); the watchtower performs its loop of duties every 4 to 6 minutes, and you will notice a distinct change in its output once you've joined the Oracle DAO.
Next Steps
Now that you've joined the Oracle DAO, take a look at the next section to learn how to test your node in this role.